

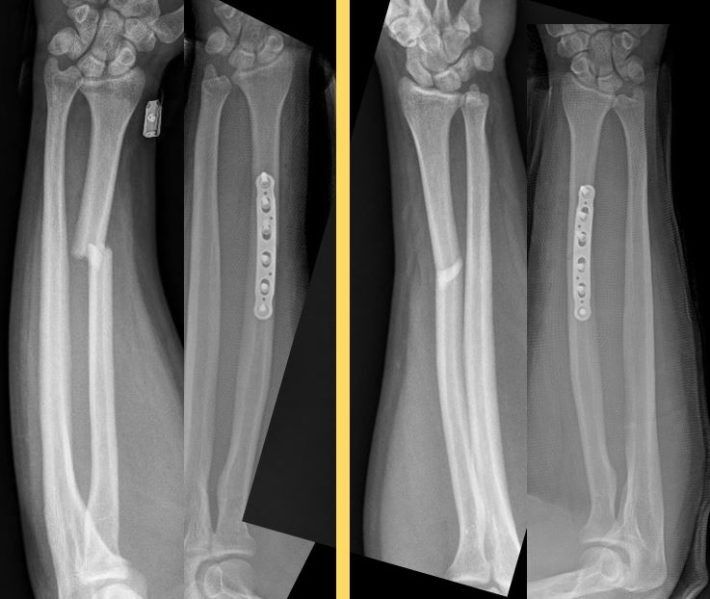
Conclusion Galeazzi fractures are inherently unstable injuries that require surgical fixation for optimal results. Postoperatively, the patient demonstrated good motion and restoration of the forearm and wrist. Results Fracture fixation was achieved intraoperatively. A case of a 36-year-old woman with a Galeazzi fracture is presented, including the diagnosis, surgical technique, and postoperative plan for rehabilitation. We discuss surgical indications and considerations, including fracture sequelae and operative approach. Methods The anatomy of, mechanism of, diagnosis of, and treatment options for the Galeazzi fracture are reviewed. Detailed step by step desription of Nonoperative treatment for Simple fracture of the radius, with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint (Galeazzi) located. Purpose This video overview and case presentation demonstrates the diagnostic and surgical approach to the treatment of the Galeazzi fracture. Chronic Galeazzi fractures are extremely rare in the literature, and late diagnosis can lead to arthrodesis, prolonged rehab, and possible suboptimal functional outcomes if not managed properly. Outcomes after surgical treatment have been demonstrated to be highly favorable, with the majority of patients experiencing positive return to function. Surgical repair of the Galeazzi fracture may also include fixation of the ulnar styloid, triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) repair, and possible fixation of the ulnar to the radius. The fracture pattern is inherently unstable and most often requires surgical treatment to prevent loss of reduction. These injuries are relatively rare, constituting <3% of pediatric forearm fractures and <7% of adult forearm fractures. Background Galeazzi fractures are fractures of the distal radial shaft with disruption of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
